Central sleep apnea (CSA) is a conditions in which you repeatedly stop breathing throughout the night because your brain periodically stops sending messages to your brain to breathe. In order to begin breathing again, your body temporarily wakes up. This cycle is called an apnea or apnea event. Due to CSA, you may have anywhere from 40 to 100+ apnea events per night. The most common scale used to measure the severity of sleep apnea is number of apneas per hour:
- Mild sleep apnea: 5-14 apneas per hour of sleep
- Moderate sleep apnea: 15-30 apneas per hour of sleep
- Severe apnea: 30+ apneas per hour of sleep
Both mild and severe CSA can lead to a high degree of sleep deprivation and associated consequences. CSA is relatively uncommon compared to the other apnea sleep condition, obstructive sleep apnea (OSA).
Forms/Risk Factors of Central Sleep Apnea
Central sleep apnea can be broken down into several forms:
- Primary Central Sleep Apnea: unknown cause
- Cheyne-Stokes Breathing Pattern: an irregular breathing pattern that results in a temporary apneas and mainly occurs in men aged 60 years or older
- Narcotic-Induced CSA: this type of CSA occurs in people who are on chronic narcotic therapy (i.e., chronic pain, or drug abuse)
- Medical Condition: medical conditions such as heart or kidney problems and abnormalities of the base of the brain where breathing is regulated
Risk factors include [Mayo Clinic]:
- Older age
- Male sex
- Heart disorders
- Narcotic use
- Stroke
Central Sleep Apnea vs. Obstructive Sleep Apnea
CSA and OSA are the most common sleep apneas. The difference between them is breathing drive. In central sleep apnea, there is not drive to breathe, or no effort put out by the brain. In obstructive sleep apnea, there is a drive, but there is a blockage preventing air from passing.
In theory, the two seem very different. However, in practice, the two are very difficult to distinguish from one another. Another difference is that OSA is much more common and has a much greater number of possible causes.
Beyond this, OSA and CSA have a lot of overlap, such as with potential consequences and symptoms.
Symptoms and Diagnosis of Central Sleep Apnea
Symptoms of CSA include [WebMD]:
- Frequent pauses in breathing at night (reported by another person)
- Gasping for air during sleep
- Morning headaches
- Excessive daytime sleepiness
- General, chronic irritability
- Difficulty staying asleep
- Chronic dry mouth at night
- Snoring (though more common in OSA)
The primary indicator of central sleep apnea is the recurrent cessation of breathing during sleep, often requiring a bed partner to notice and report these episodes. If you lack a partner to observe these pauses, your symptoms may prompt you or your healthcare provider to consider a sleep study for further evaluation. A formal diagnosis of CSA typically involves undergoing a comprehensive sleep study.
Side Effects of Central Sleep Apnea
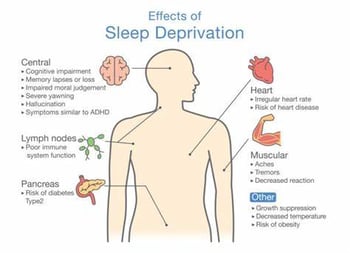 Untreated sleep apnea generally results in chronic sleep deprivation. Chronic sleep deprivation can hae the following negative effects:
Untreated sleep apnea generally results in chronic sleep deprivation. Chronic sleep deprivation can hae the following negative effects:
- Lower quality of life
- Shorter life expectancy
- Risks of medical conditions such as:
- Heart disease
- High blood pressure
- Diabetes
- Depression
- Mood disorders
Treatment Options for Central Sleep Apnea
Fortunately, treatment options for CSA are generally very successful. Most include positive airway pressure therapy, which helps counter closed airways. A common therapy is continuous positive airway pressure, or CPAP, which is a machine that provides this therapy throughout the night. Other management options are lifestyle changes like weight loss, abstinence from drugs, cessation in smoking, management of chronic conditions, and reducing stroke risks through healthy diet and exercise.
If you live in Alaska, and are concerned that you or a loved one has a sleeping disorder, please click the orange button below to take a free online sleep test and talk with one of our sleep health professionals.


