What is Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA)?
Obstructive sleep apnea is a sleep disorder and potentially serious medical condition. OSA causes you to stop breathing for 20+ seconds many times throughout the night, anywhere from 40 to hundreds of times. Each time you stop breathing you rouse yourself out of sleep to begin breathing again. However, this process is subconscious, and prevents you from entering the deep, restorative stages of sleep. In the morning you will not remember rousing, though you will certainly feel the effects of not having any restful sleep!
The reason OSA causes you to stop breathing is because your throat becomes obstructed:
- The breathing muscles in the back of your throat relax
- This causes the back of your throat to collapse fully or partially
- Your collapsed throat, sometimes with the assistance of tonsils or tongue, blocks your airway
- Your body wakes from sleep to resume breathing
- You do not remember waking up in the morning
Each blockage/arousal cycle is called an apnea or apnea event. OSA can lead to moderate or catastrophic sleep deprivation, with well-known medical side effects.
OSA can be mild, moderate or severe depending on how many apneas you experience.
Does OSA Have Different Severity Levels?
Obstructive sleep apnea has a different severity depending on how many apneas are experienced per hour.
- Mild: 5-14 apneas per hour of sleep
- Moderate: 15-30 apneas per hour of sleep
- Severe: 30+ apneas per hour of sleep
The important implication here is that even mild OSA causes you to rouse several dozen times per night in a BEST case scenario, but can be upward of 240 times per night or more.
Severe sleep apnea may cause more noticeable symptoms than mild OSA, and the treatments may be different as well, but the risk factors are generally the same for mild, moderate, and severe sleep apnea.
What do Symptoms of OSA Look Like?
Obstructive sleep apnea can go unnoticed for many years, especially in the case where you do not have a bed partner. A bed partner can be instrumental in identifying obstructive sleep apnea because the two hallmark symptoms are things the person with OSA will not notice on their own:
- Repeated episodes of not breathing throughout the night
- Chronic, loud snoring
Other symptoms that are common for those with OSA include:
- Restless sleep
- Morning headaches
- Daytime fogginess
- Severe daytime sleepiness
- Chronic irritability
- Depression/anxiety
It is likely that even if you don’t have a bed partner, someone will make you aware of your chronic snoring. If this is the case, you should pay attention to other symptoms to try and identify whether or not you simply have a snoring issue or if there are other causes at work.
Is OSA Dangerous - are there Risks?
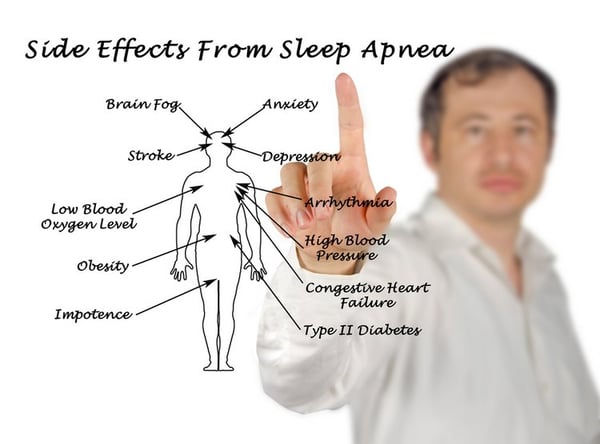
Risk of OSA are numerous and can be serious - they are caused because of chronic sleep deprivation over periods of time. Some of the main risks are:
- High blood pressure
- Diabetes
- Stroke
- Heart disease
- Depression
- Reduced cognitive performance
- Reduced stress management
- Shorter life expectancy
- Lower quality of life
- Lower performance in many areas of life
Interestingly, the risk factors remain the same whether you have mild or severe sleep apnea, though in more severe cases the symptoms may express themselves quicker and in greater severity.
Can OSA Be Treated?
For most cases of OSA, CPAP therapy is what is used to treat OSA. Note however, that depending on your physical health and lifestyle, CPAP therapy may be prescribed only after other options are explored [resmed] such as:
- Lifestyle changes
- Losing weight
- Changing sleep position
- Medication changes
- Surgery (rare)
CPAP therapy is a technique used via a CPAP machine. A CPAP device/machine stands for Continuous Positive Airway Pressure and is the primary component of CPAP therapy and sleep apnea treatment, as it is extremely effective at preventing lapses in breathing (i.e., OSA).
If you live in Alaska, and are concerned that you or a loved one has sleep apnea or has already been diagnosed, please take this free online sleep test.